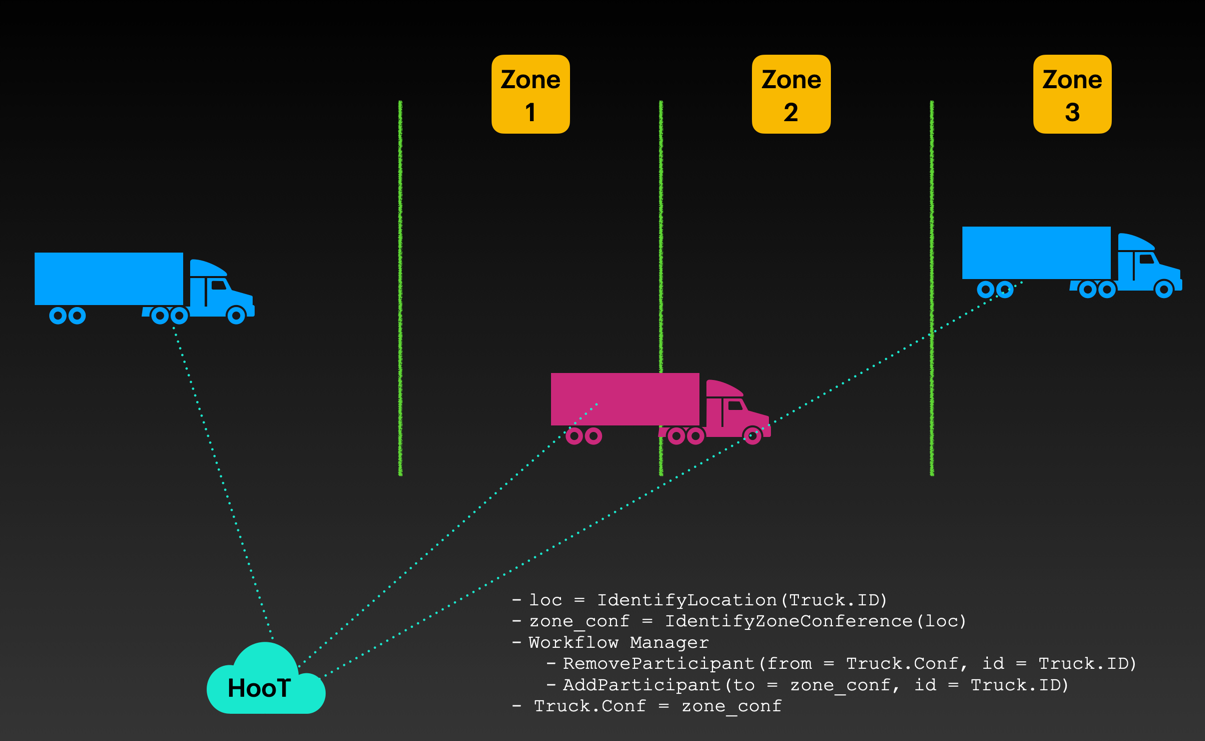
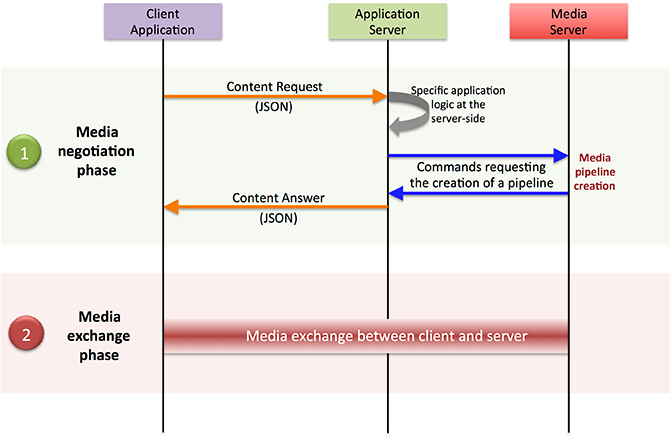
HooT.mx, a robust collaboration tool, can play a pivotal role in large-scale warehouse automation when deployed on Kubernetes across multiple clouds, such as Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Azure, and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
In this environment, the warehouse is seen as a complex system with numerous actors and processes that must be coordinated effectively to optimize the flow of goods. HooT.mx, originally designed for web conferencing and collaboration, has several features that can be natively applied to manage and improve this flow.
Hoot.mx in Warehouse Automation:
Real-time Collaboration: Warehouse operations involve various entities, including staff members, automated machines, and management systems. HooT.mx can foster real-time communication and collaboration, enabling seamless coordination between different entities. Real-time data sharing, messaging, and the ability to initiate quick calls can speed up decision-making and reduce downtime.
Video and Audio Streams: The video and audio streaming capabilities of HooT.mx can be used for real-time surveillance and remote troubleshooting. This helps in monitoring the goods' flow and handling unexpected disruptions promptly.
Screen Sharing & Whiteboard: These features can be used for training purposes, equipment maintenance demonstrations, and strategic planning for optimizing goods flow patterns.
Recording & Playback: Sessions can be recorded and played back for training or for post-mortem analysis in case of disruptions.
Use-Case
I'll create a simple use case where the warehouse staff and the warehouse manager are collaborating in real-time to handle a task, such as managing inventory, using HooT.mx. The warehouse staff can communicate via HooT.mx, and the warehouse manager can monitor and coordinate the tasks in real-time.
First, let's start with a simple textual flow diagram using Mermaid.js:
graph TB
A(Staff1) -->|HooT.mx| B((Central Server))
C(Staff2) -->|HooT.mx| B
D(Staff3) -->|HooT.mx| B
E(Manager) -->|HooT.mx| B
B -->|Data Sync| F[Inventory Management System]
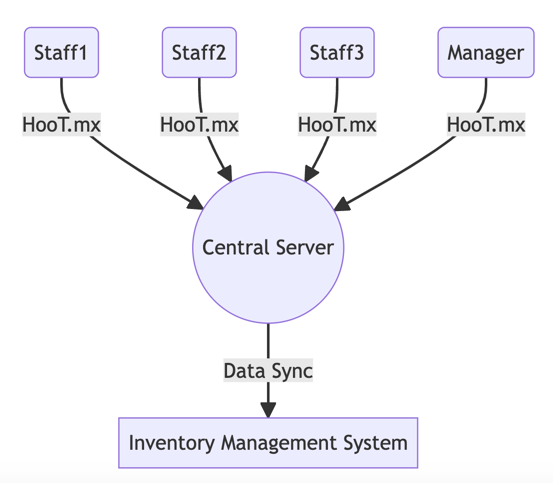
In this diagram, each warehouse staff (Staff1, Staff2, and Staff3) and the Manager are communicating through HooT.mx, which is synced with a Central Server. This Central Server also communicates and syncs with an Inventory Management System, enabling real-time collaboration.
Now, let's delve into how this collaboration can be coded. We'll use JavaScript/Node.js for this example. Please note that these are simplified and illustrative examples, as actual implementation with HooT.mx would require usage of its specific APIs and would likely be more complex:
First, we would need to set up the HooT.mx connections:
const hoot = require('hoot-mx');
let centralServer = new hoot.Server({
host: 'central-server',
port: 443,
secure: true
});
let staff1 = new hoot.User('Staff1');
let staff2 = new hoot.User('Staff2');
let staff3 = new hoot.User('Staff3');
let manager = new hoot.User('Manager');
centralServer.addUser(staff1);
centralServer.addUser(staff2);
centralServer.addUser(staff3);
centralServer.addUser(manager);
Then, we would set up the real-time collaboration, using the data streams to sync the Inventory Management System:
// Staff1 reports an inventory update
staff1.sendMessage('Update: Item X is out of stock.');
// The message is received by the Central Server and pushed to the Manager
centralServer.on('message', (user, message) => {
if(user.name.startsWith('Staff')) {
manager.sendMessage(`${user.name} reports: ${message}`);
}
});
// The manager coordinates the tasks
manager.on('message', (user, message) => {
if(user.name.startsWith('Staff')) {
user.sendMessage('Got your update. Please restock Item X.');
}
});
// The Central Server updates the Inventory Management System
centralServer.on('message', (user, message) => {
if(user.name.startsWith('Staff') && message.startsWith('Update:')) {
inventorySystem.updateStock(message);
}
});
This code snippet illustrates how the warehouse staff and the manager can collaborate in real-time, using HooT.mx, to manage inventory. In the real-world implementation, the actual HooT.mx APIs would be used, and the code would likely be much more complex, involving handling of video and audio streams, user authentication, error handling, and more.
Scaling HooT.mx with Kubernetes on Multi-cloud:
The adoption of Kubernetes allows for easy scaling and management of HooT.mx services across multiple clouds. Kubernetes can manage the lifecycle of HooT.mx instances, handling scaling, failover, and updates seamlessly.
Multi-cloud deployment on GCP, Azure, and AWS ensures resilience and availability. Each cloud provider has unique strengths and can provide different geographic coverage. Using all three can distribute risk and provide a more reliable, robust service.
Applying AI/ML to Media Streams:
AI/ML can add significant value to the media streams flowing through HooT.mx.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine Learning algorithms can analyze video and audio streams to predict potential disruptions, allowing for proactive adjustments to the flow of goods.
Let's clarify this by integrating HooT.mx, which is a collaboration platform, into our warehouse automation use case.
HooT.mx can serve as a central hub for real-time data sharing and communication between different teams managing the warehouse. It can also facilitate the presentation and interpretation of the predictive analytics results in an interactive, collaborative environment.
Suppose there's a central team of data scientists or analysts who are in charge of maintaining and interpreting the machine learning models used for predictive analytics. When these models detect a potential disruption in the warehouse, the central team could quickly communicate this information to the relevant warehouse team using HooT.mx.
The warehouse team could then view the relevant video streams, the detected anomalies, and the predicted future state of the warehouse in real-time on HooT.mx. They can discuss the situation, share their insights, and decide on the best course of action.
Additionally, they could also leverage the features of HooT.mx such as audio and video conferencing, screen sharing, and document sharing to facilitate their discussions and decision-making process. They can also record their sessions for future reference and training purposes.
Here's a simplified representation of this process:
graph LR
A[Video Stream from Cameras] --> B[CNN Model]
B --> C[Detected Anomalies]
C --> D[Predictive Model]
D --> E[Predicted Future State]
E --> F[HooT.mx Collaboration Platform]
F --> G[Warehouse Team]
In terms of code, we could integrate HooT.mx into our workflow using its API. We would send the output of the predictive model (i.e., the predicted future state of the warehouse) to HooT.mx. The relevant warehouse team would then receive a notification and can start a HooT.mx session to discuss the situation:
import requests
# Use CNN model to detect anomalies in video stream
anomalies = cnn.predict(test_images)
# Use predictive model to predict future state based on detected anomalies
predicted_future_state = predictive_model.predict(anomalies)
# Send predicted future state to HooT.mx
url = "https://api.hoot.mx/send_notification"
data = {"predicted_future_state": predicted_future_state.tolist()}
headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_HOOT_MX_API_KEY"}
response = requests.post(url, json=data, headers=headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("Notification sent to HooT.mx successfully.")
else:
print("Failed to send notification to HooT.mx.")
In this code snippet, we first detect anomalies in the video stream and predict the future state of the warehouse as before. Then we send a notification with the predicted future state to HooT.mx using its API. The warehouse team then receives this notification and can start a HooT.mx session to discuss the situation.
This integration of HooT.mx into the predictive analytics workflow allows for real-time collaboration and quick decision-making, which are crucial in a high-flow warehouse environment.
- Image and Sound Recognition: AI can be used to identify specific visual or auditory cues that may indicate issues with machinery, congestion in certain areas, or other potential disruptions to the flow of goods.
Let's dive deeper into how AI can be used for image and sound recognition in warehouse automation.
To start, let's understand what we mean by image and sound recognition in the context of a warehouse. Image recognition refers to the ability of AI to identify and classify visual elements, such as the presence of specific objects (e.g., boxes, pallets, forklifts) or the detection of unusual patterns (e.g., congestion, misplaced items). On the other hand, sound recognition refers to the ability of AI to detect and interpret audio signals, such as the sound of machinery or environmental noises.
With HooT.mx, these capabilities can be greatly enhanced. The platform's ability to stream audio and video in real-time means that AI models can analyze data as it comes in.
Let's imagine a scenario where we have cameras and microphones installed in the warehouse. The cameras can capture the visual aspects of the warehouse operations, while the microphones can record the ambient sounds.
Image Recognition
A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) can be used for real-time image recognition tasks. It can analyze the live video streams from the cameras to identify potential issues, such as the detection of a forklift operating in an unauthorized area or congestion due to misplaced pallets.
Sound Recognition
SAI model like a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) can analyze the audio streams from the microphones. This model can detect abnormal machine noises that could indicate potential equipment failures.
Upon detection of an anomaly, whether visual or auditory, a notification can be sent to the relevant team through HooT.mx. This allows for instant, coordinated action to resolve the issue.
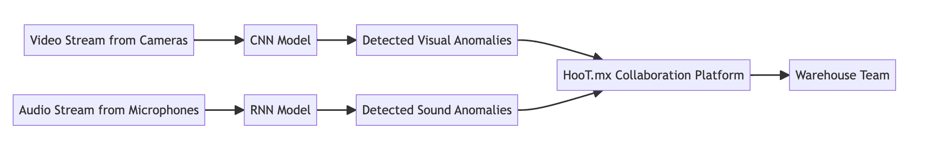
Here's a mermaid representation of the process:
graph LR
A[Video Stream from Cameras] --> B[CNN Model]
B --> C[Detected Visual Anomalies]
C --> F[HooT.mx Collaboration Platform]
F --> G[Warehouse Team]
H[Audio Stream from Microphones] --> I[RNN Model]
I --> J[Detected Sound Anomalies]
J --> F
In terms of code, we could create an AI system that combines both image and sound recognition capabilities. The following pseudocode gives a rough idea:
import requests
# Image Recognition
image_anomalies = cnn.predict(live_video_stream)
# Sound Recognition
sound_anomalies = rnn.predict(live_audio_stream)
# Analyze anomalies
combined_anomalies = analyze_anomalies(image_anomalies, sound_anomalies)
# If anomalies detected, send to HooT.mx
if combined_anomalies:
url = "https://api.hoot.mx/send_notification"
data = {"combined_anomalies": combined_anomalies.tolist()}
headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_HOOT_MX_API_KEY"}
response = requests.post(url, json=data, headers=headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("Notification sent to HooT.mx successfully.")
else:
print("Failed to send notification to HooT.mx.")
With such a system, we could provide real-time monitoring and instant notifications of potential disruptions in warehouse operations. HooT.mx can serve as the central hub for relaying these notifications and facilitating swift responses.
- Process Optimization: Machine Learning can optimize goods flow by analyzing historical and real-time data from the HooT.mx streams. Process optimization in warehouse operations is a complex task that involves analyzing multiple variables such as incoming orders, inventory status, equipment status, and more. However, by integrating machine learning (ML) with real-time data from HooT.mx streams, we can create a dynamic system capable of self-optimization.
For instance, by analyzing historical data, ML algorithms can learn patterns and trends, such as busy hours, peak days, most frequent order types, etc. This information can be used to create predictive models, allowing the system to anticipate future demands and adjust resources accordingly.
Real-time data from HooT.mx streams brings another layer of adaptability. As the HooT.mx platform captures live audio-visual data, an ML model can continuously monitor this feed to identify changes in the operational environment.
Let's create a hypothetical scenario where we have a warehouse where goods flow is dependent on several factors including order type, time of day, available workforce, and operational status of machinery. We can leverage ML and HooT.mx to optimize the goods flow.
Real-time Data Analysis and Prediction
A machine learning model, such as a Random Forest or a Gradient Boosting model, can analyze the live data streams coming from HooT.mx. The model can predict potential bottlenecks based on variables such as order type, time of day, and equipment status.
Process Adjustment
Based on the predictions, the system can make real-time adjustments to the workflow. For example, it might reassign workers, alter the sequence of operations, or adjust machinery settings.
Continuous Learning
As more data is generated and captured by HooT.mx, the model can continuously learn and improve its predictions, making the system increasingly efficient over time.
Here's a mermaid representation of this process:
graph LR
A[Historical Data] --> B[ML Model]
C[Real-time Data from HooT.mx] --> B
B --> D[Process Prediction]
D --> E[Process Adjustment]
E --> F[Optimized Goods Flow]
F --> G[Data Feedback to HooT.mx]
G --> B
In terms of code, you might create a system that leverages ML for process optimization like this:
import requests
# Fetch historical data
historical_data = fetch_data_from_db()
# Train ML model
model = train_model(historical_data)
# Fetch real-time data from HooT.mx
real_time_data = fetch_data_from_hoot_mx()
# Predict process adjustment
predicted_adjustment = model.predict(real_time_data)
# If adjustment needed, apply changes
if predicted_adjustment:
url = "https://api.your_warehouse_management_system/apply_adjustment"
data = {"adjustment": predicted_adjustment.tolist()}
headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_WAREHOUSE_MANAGEMENT_SYSTEM_API_KEY"}
response = requests.post(url, json=data, headers=headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("Process adjustment applied successfully.")
else:
print("Failed to apply process adjustment.")
# Feedback data to HooT.mx for further improvement
feedback_data_to_hoot_mx(real_time_data, predicted_adjustment)
With HooT.mx providing a stream of real-time data, ML can not only analyze and predict but also continually learn and refine its understanding, leading to more efficient goods flow in the warehouse.
In conclusion, a well-deployed HooT.mx system, combined with the scalability of Kubernetes on a multi-cloud environment and the intelligence of AI/ML, could offer a significant boost in efficiency and productivity for large-scale warehouse operations.